Table Of Content
Speaking up is one way to multiply impact and create change on a much bigger scale. Over the course of the 20th century, precipitation increased in eastern parts of North and South America, northern Europe, and northern and central Asia. However, it has decreased in parts of Africa, the Mediterranean, and southern Asia.
Climate change: evidence and causes - Royalsociety
Climate change: evidence and causes.
Posted: Tue, 27 Feb 2024 05:02:55 GMT [source]
The gas in this exploding mine is odorless, colorless—and could transform the world
All selected applicants intend to invest in local, clean energy workforce development programs to expand equitable pathways into family-sustaining jobs for the communities they are designed to serve. But even the 70 percent that gets through doesn't stay on Earth forever (otherwise, the Earth would become a blazing fireball). The things around the planet that absorb the sun's heat eventually radiate a portion of that heat (radiation) back out at a different wavelength, like your car seats and dashboard do. You've probably noticed that your car is always much hotter inside than the outside temperature if it's been sitting there for a while.
Solutions for reducing greenhouse gas emissions
By adhering to International Standards to measure and report our emissions, we guarantee that our efforts are as effective and coordinated as possible. For just as the greenhouse gas emissions from a century ago still contribute to the climate change we see today, the emissions we release today will continue to impact us long into the future. IndustryAccording to the IPCC, about one-fifth of global human-driven emissions come from the industrial sector, which includes the manufacturing of goods and raw materials (like cement and steel), food processing, and construction. In 2021, industry accounted for 23 percent of U.S. man-made emissions, of which the majority was carbon dioxide, although methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases were also released.
What is the greenhouse effect?
China is responsible for around 15 percent of the cumulative global total, but currently emits more carbon dioxide annually than any other country (31 percent). Together, the major economies of China, the United States (14 percent), the EU-28 (8 percent), India (7 percent), and Russia (5 percent) represent almost 65 percent of annual global emissions. Today and historically, African countries and small island nations, some of the regions most vulnerable to the harsh impacts of climate change, contribute the least. The roots of the greenhouse effect concept lie in the 19th century, when French mathematician Joseph Fourier calculated in 1824 that the Earth would be much colder if it had no atmosphere. In 1896, Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius was the first to link a rise in carbon dioxide gas from burning fossil fuels with a warming effect.
Radiative balance
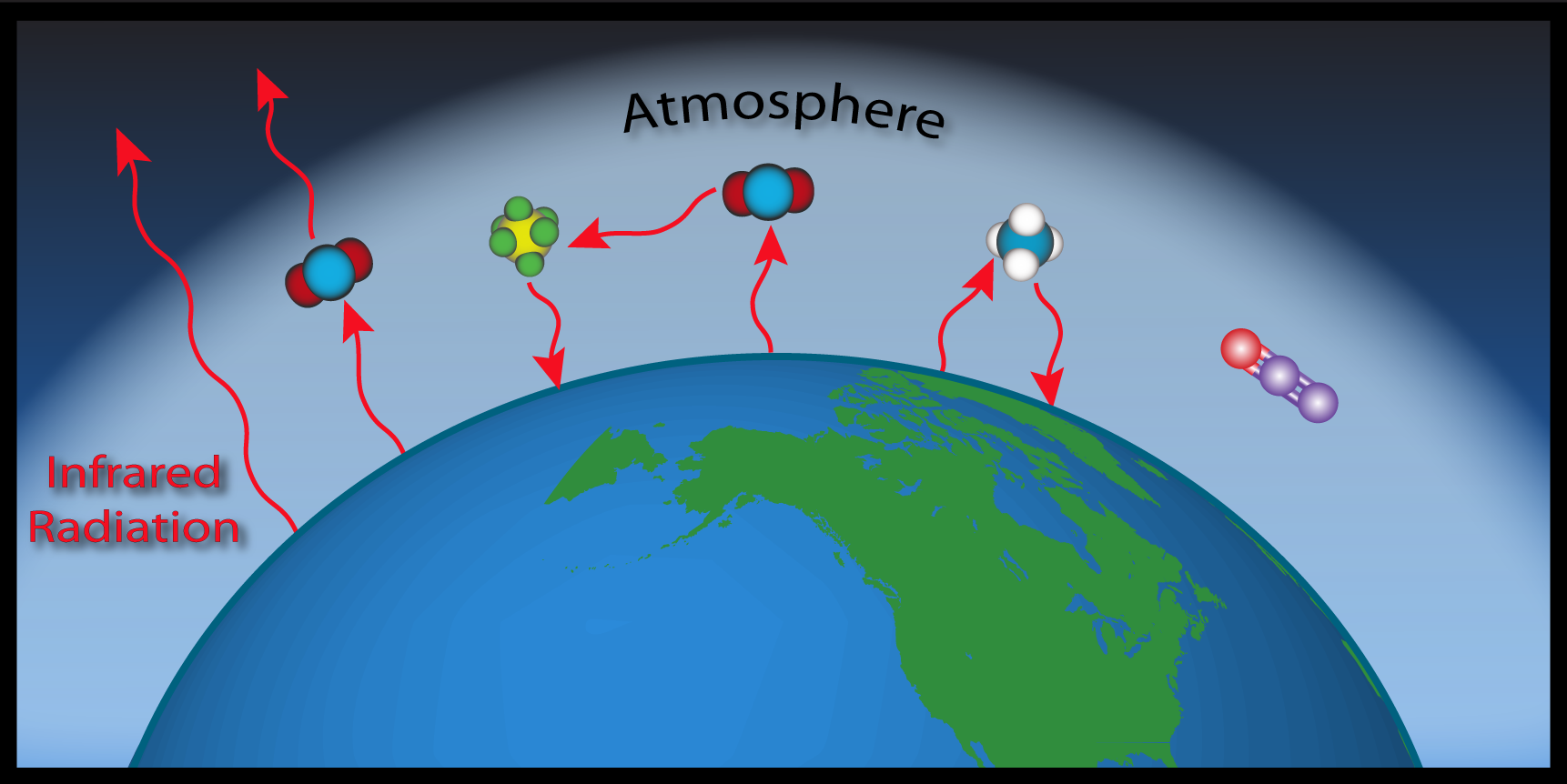
UV radiation has a shorter wavelength and a higher energy level than visible light, while IR radiation has a longer wavelength and a weaker energy level. About 30 percent of the radiation striking Earth's atmosphere is immediately reflected back out to space by clouds, ice, snow, sand and other reflective surfaces, according to NASA. The remaining 70 percent of incoming solar radiation is absorbed by the oceans, the land and the atmosphere. As they heat up, the oceans, land and atmosphere release heat in the form of IR thermal radiation, which passes out of the atmosphere and into space. By increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, we’re amplifying Earth’s natural greenhouse effect and turning up the dial on global warming and climate change. Greenhouse gases are – for the most part – a natural phenomenon; they trap heat from sunlight reflecting off Earth’s surface.
List gases which are responsible for the greenhouse effect.
Oil and gas extraction, coal mining, and waste landfills account for 55 per cent of human-caused methane emissions. Approximately 32 per cent of human-caused methane emissions are attributable to cows, sheep and other ruminants that ferment food in their stomachs. Manure decomposition is another agricultural source of the gas, as is rice cultivation.
Fossil Fuel Combustion and the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Gas concentrations hit record high. Again. - World Meteorological Organization WMO
Greenhouse Gas concentrations hit record high. Again..
Posted: Wed, 15 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Solar for All will expand existing low-income solar programs and launch new ones. The 60 selected applicants will serve households in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and territories, as well as increase access to solar for Tribes. EPA has selected 49 state-level awards totaling approximately $5.5 billion, six awards to serve Tribes totaling over $500 million, and five multistate awards totaling approximately $1 billion.
The Causes of Climate Change
This Earth system model is one way to represent the essential processes and interactions related to the greenhouse effect. Hover over the icons for brief explanations; click on the icons to learn more about each topic. There are a few ways that the relationships among these topics can be represented and explained using the Understanding Global Change icons (download examples). Discover why the climate and environment changes, your place in the Earth system, and paths to a resilient future. About a third of the Sun's energy (30%) is reflected back into space.
Greenhouse gases and global warming
Without this absorption, Earth's surface would have an average temperature of −18 °C (−0.4 °F). However, because some of the radiation is absorbed, Earth's average surface temperature is around 15 °C (59 °F). Thus, the Earth's greenhouse effect may be measured as a temperature change of 33 °C (59 °F). If extra amounts of greenhouse gases are added to the atmosphere, such as from human activities, then they will absorb more of the infra-red radiation. The Earth's surface and the lower atmosphere will warm further until a balance of incoming and outgoing radiation is reached again (the emission of infra-red radiation increases as the temperature of the emitting body rises).
A climate driver with a positive RF value indicates that it has a warming effect on the planet; a negative value represents cooling. Water vapor is actually the world's most abundant greenhouse gas, but it is not tracked the same way as other greenhouse gases because it is not directly emitted by human activity and its effects are not well understood. Similarly, ground-level or tropospheric ozone (not to be confused with the protective stratospheric ozone layer higher up) is not emitted directly but emerges from complex reactions among pollutants in the air.
The greenhouse effect, which influences Earth’s average temperature, affects many of the processes that shape global climate and ecosystems. This model shows some of the other parts of the Earth system that the greenhouse effect influences, including the water cycle and water temperature. In agreements like the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement, the world has begun to take action to try to curb global greenhouse gas emissions. It remains to be seen whether these efforts will succeed in averting disaster or will prove to be too little too late. We often hear about the "greenhouse effect" in the negative context of global warming — it's why the glaciers are melting and climate patterns are undergoing dangerous shifts. But the greenhouse effect is not actually a bad thing in itself — it's a crucial and positive part of Earth's energy balance.
On Mars, greenhouse gases such as water and carbon dioxide might have been released during ancient impact events. Some scientists speculate that such wallops could have raised Mars' overall temperature enough for the planet to have liquid water on its surface for significant lengths of time. However, because Mars is smaller than Earth, it's gravitational pull is weaker. Therefore, these gases drifted away, and eventually, the Red Planet reverted back to the cold and dry world it is today. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth’s temperature would be below freezing. However, Earth’s greenhouse effect is getting stronger as we add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
Some of the heat will head away from the Earth, some of it will be absorbed by another greenhouse gas molecule, and some of it will wind up back at the planet’s surface again. With more greenhouse gases, heat will stick around, warming the planet. Solar energy absorbed at Earth’s surface is radiated back into the atmosphere as heat. As the heat makes its way through the atmosphere and back out to space, greenhouse gases absorb much of it. Greenhouse gases are more complex than other gas molecules in the atmosphere, with a structure that can absorb heat. They radiate the heat back to the Earth's surface, to another greenhouse gas molecule, or out to space.
Even burning all of the planet’s fossil fuel resources, according to some scientists, would not necessarily take us down the road toward a climate meltdown. By studying why Venus’s climate went in such a different direction with regard to habitability, we can probably learn valuable lessons about climate change – and avoid reaching the point of no return. The good news is that we have the ability to rein in runaway greenhouse gas emissions.

No comments:
Post a Comment