Table Of Content
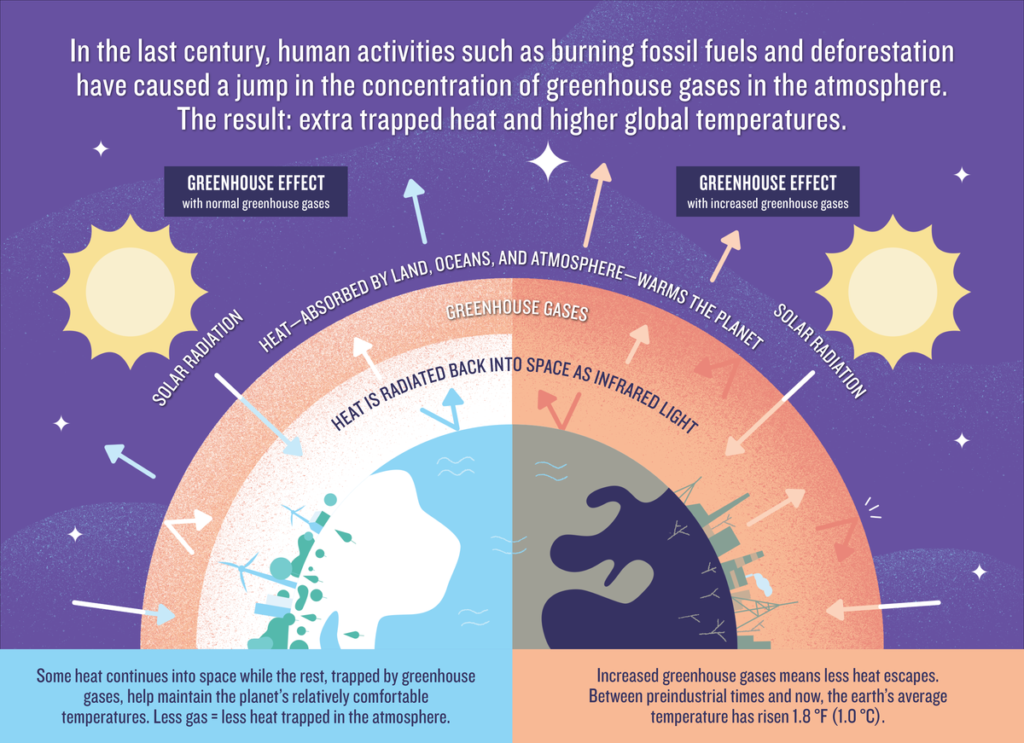
About half the light energy reaching Earth's atmosphere passes through the air and clouds to the surface, where it is absorbed and radiated in the form of infrared heat. About 90% of this heat is then absorbed by greenhouse gases and re-radiated, slowing heat loss to space. With more greenhouse gases in the air, heat passing through on its way out of the atmosphere is more likely to be stopped.
‘It’s now or never’: UN climate report’s 4 urgent takeaways
Geoengineering Is Easier Said Than Done] "You remove the water vapor, you remove the humidity and you prevent the normal cirrus cloud formation," Lohmann said. Tell President Biden and Congress to slash climate pollution and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Shifting to renewable energy, putting a price on carbon, and phasing out coal are all important elements in reducing GHG emissions. Ultimately, stronger emission-reduction targets are necessary for the preservation of long-term human and environmental health. Coal, oil, and natural gas continue to power many parts of the world.
Greenhouse gases and climate change
Eventually, the vibrating molecules release the radiation, which will likely be absorbed by another greenhouse gas molecule. Most of the gas in the atmosphere is nitrogen and oxygen, which cannot absorb heat and contribute to the greenhouse effect. Matter emits thermal radiation in an amount that is directly proportional to the fourth power of its temperature. Some of the radiation emitted by the Earth's surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases and clouds.
The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming - Columbia University
The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming.
Posted: Sun, 07 Jan 2024 02:00:30 GMT [source]
What are the major greenhouse gases?
The greenhouse effect describes a similar phenomenon on a planetary scale but, instead of the glass of a greenhouse, certain gases are increasingly raising global temperatures. When Venus' oceans vaporized, its planetary plate tectonics would have ground to a halt, as there was no water left to help lubricate the shifting of geological plates. The increasingly thick atmosphere might have created a drag on Venus' rotation period, leading to its bizarrely slow spin, in which a year goes by with only two days passing.
Millions more people in countries like Bolivia, Peru, and India depend on glacial meltwater for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power. In the solar system, apart from the Earth, at least two other planets and a moon also have a greenhouse effect. There are sometimes misunderstandings about how the greenhouse effect functions and raises temperatures. A given wavelength of radiation may also be said to have an effective emission altitude, which is a weighted average of the altitudes within the radiating layer. Barking up the Wrong TreeSpruce bark beetles in the U.S. state of Alaska have had a population boom thanks to 20 years of warmer-than-average summers. The insects have managed to chew their way through 1.6 million hectares (four million acres) of spruce trees.

Evidence Shows That Current Global Warming Cannot Be Explained by Solar Irradiance
While around 30 percent of the solar energy—the light and heat from the sun—that reaches our world is reflected back into space, the rest is either absorbed by the atmosphere or the earth’s surface. This process, which is constantly happening around the globe, warms the planet. This heat is then radiated back up in the form of invisible infrared radiation. While some of this infrared light continues on into space, the vast majority gets absorbed by atmospheric gases, known as greenhouse gases, causing further warming. Although the greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon, it is possible that the effect could be intensified by the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as the result of human activity.
While other planets in Earth's solar system are either scorching hot or bitterly cold, Earth's surface has relatively mild, stable temperatures. Earth enjoys these temperatures because of its atmosphere, which is the thin layer of gases that cloak and protect the planet. Several billion years ago, a runaway greenhouse effect turned all surface water into vapour, which then leaked slowly into space. This occurs when a planet absorbs more energy from the sun than it can radiate back to space. Earth's atmosphere keeps much of the Sun's energy from escaping into space.
Sometimes the greenhouse effect is quantified as a temperature difference. This temperature difference is closely related to the quantities above.
Perhaps the biggest, most obvious effect is that glaciers and ice caps melt faster than usual. One cannot predict the relative sizes of the greenhouse effects on different bodies simply by comparing the amount of greenhouse gases in their atmospheres. This is because factors other than the quantity of these gases also play a role in determining the size of the greenhouse effect.
Carbon is the main element in these fuels and, when they’re burned to generate electricity, power transportation, or provide heat, they produce CO2. Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane and nitrous oxide are the major GHGs to worry about. CO2 stays in the atmosphere for up to 1,000 years, methane for around a decade, and nitrous oxide for approximately 120 years. Simplified models are sometimes used to support understanding of how the greenhouse effect comes about and how this affects surface temperature. Last week, Yousaf abruptly ended a power-sharing agreement with the Greens, embarrassing the party's two government ministers who had arrived for a Cabinet meeting.
A complete list of the selected applicants can be found on EPA’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund Solar for All website. In simple words, increasing the greenhouse effect gives rise to a runaway greenhouse effect which would increase the temperature of the earth to such an extent that no life will exist in the near future. Ozone Layer protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun.
Atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide—the most dangerous and prevalent greenhouse gas—are at the highest levels ever recorded. Greenhouse gas levels are so high primarily because humans have released them into the air by burning fossil fuels. The gases absorb solar energy and keep heat close to Earth's surface, rather than letting it escape into space. Greenhouse gases consist of carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapor. Water vapor, which reacts to temperature changes, is referred to as a 'feedback', because it amplifies the effect of forces that initially caused the warming.
But higher concentrations of greenhouse gases, and carbon dioxide (CO2) in particular, are causing extra heat to be trapped and average global temperatures to rise. For most of the past 800,000 years—much longer than human civilization has existed—the concentration of CO2 in our atmosphere was roughly between 200 and 280 parts per million. (In other words, there were 200 to 280 molecules of the gases per million molecules of air.) But in the past century, that concentration has jumped. In 2013, driven up largely by the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, CO2 in the earth’s atmosphere surpassed 400 parts per million—a concentration not seen on the planet for millions of years. As of 2023, it has reached more than 420 parts per million, which is 50 percent higher than preindustrial levels. Sunlight, with the natural greenhouse effect process, makes the earth habitable.

No comments:
Post a Comment